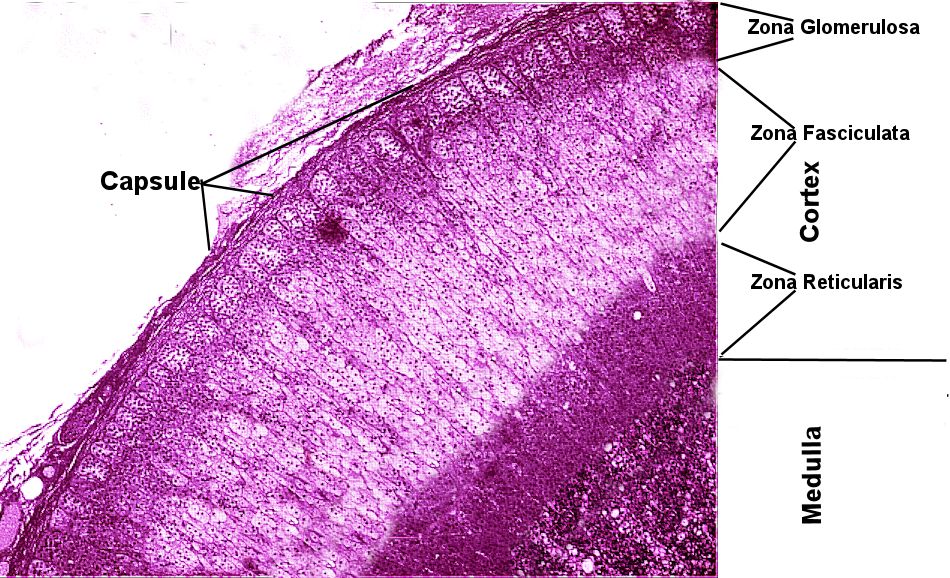
This page has endocrine histology of the adrenal gland under low power. The adrenal gland has 2 parts. The center of the adrenal gland is called the adrenal medulla and composed of nervous tissue. Axons from the sympathetic nervous system stimulate chromaffin cells to produce adrenalin (epinephrine) and noradrenalin (norepinephrine). These two hormones have the same effect as the neurotransmitters of the same name; however, the effects are much longer lasting because they are released more into the blood.
The adrenal cortex is the outside and produces steroid hormones. In reality, the adrenal cortex produces over 20 different steroid hormones and stimulation of the cortex by ACTH (made in the pituitary) causes an increase in production of all of them. The cortex can be divided into 3 visible zones. The outermost zone is called the zona glomerulosa which produces aldosterone. Aldosterone causes you to retain sodium in the kidneys and as a result you retain water as well. The second and largest of the zones is the zona fasciculata. This zone produces hormones that help us deal with stress called glucocorticoids, mainly cortisol. The glucocorticoids increase blood glucose, fatty acid, and amino acid levels thus providing the body with ready energy sources needed for emergency situations or repair. The last zone is called the zona reticularis. It is a relatively small region and is responsible for creating sex hormones
Slides which were taken by bio 139 students from spring of 2018 to fall of 2019 are in the right hand side and your lab book's picture is on the left hand side. Compare those pictures to the lab book pictures by scrolling trough hte student pictures using the black arrows. Then draw the histology as instructed by your teacher.
| Lab Book Image | Student Images |
|---|---|

|
Adrenal Gland Low Power |