Supporting Connective Tissue Histology | Histology Home Page | Site Home Page
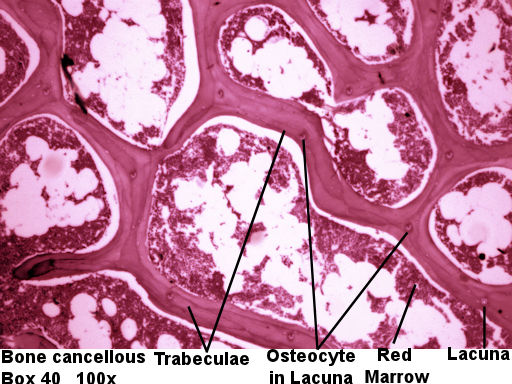
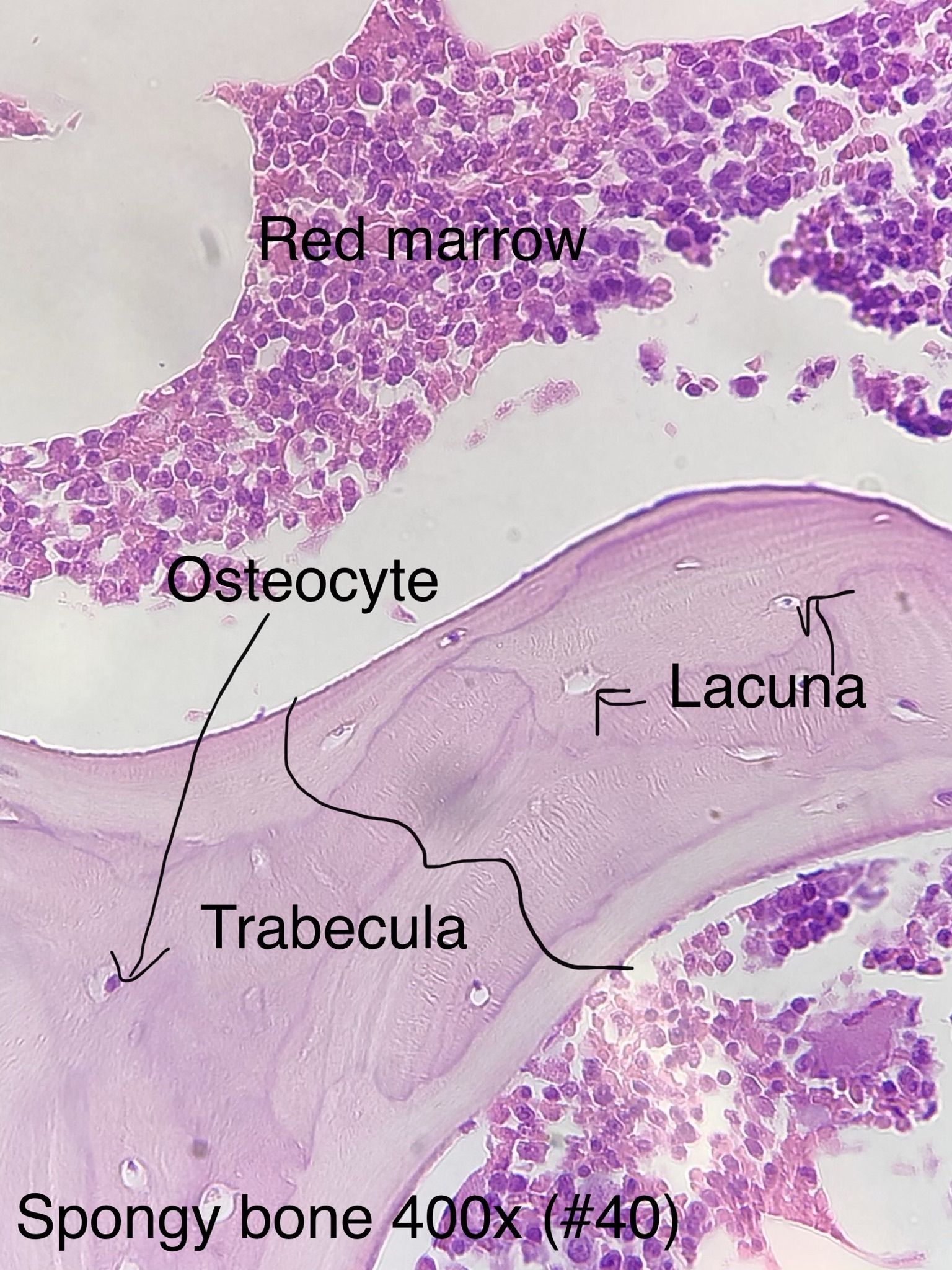
Spongy Bone Conective Tissue
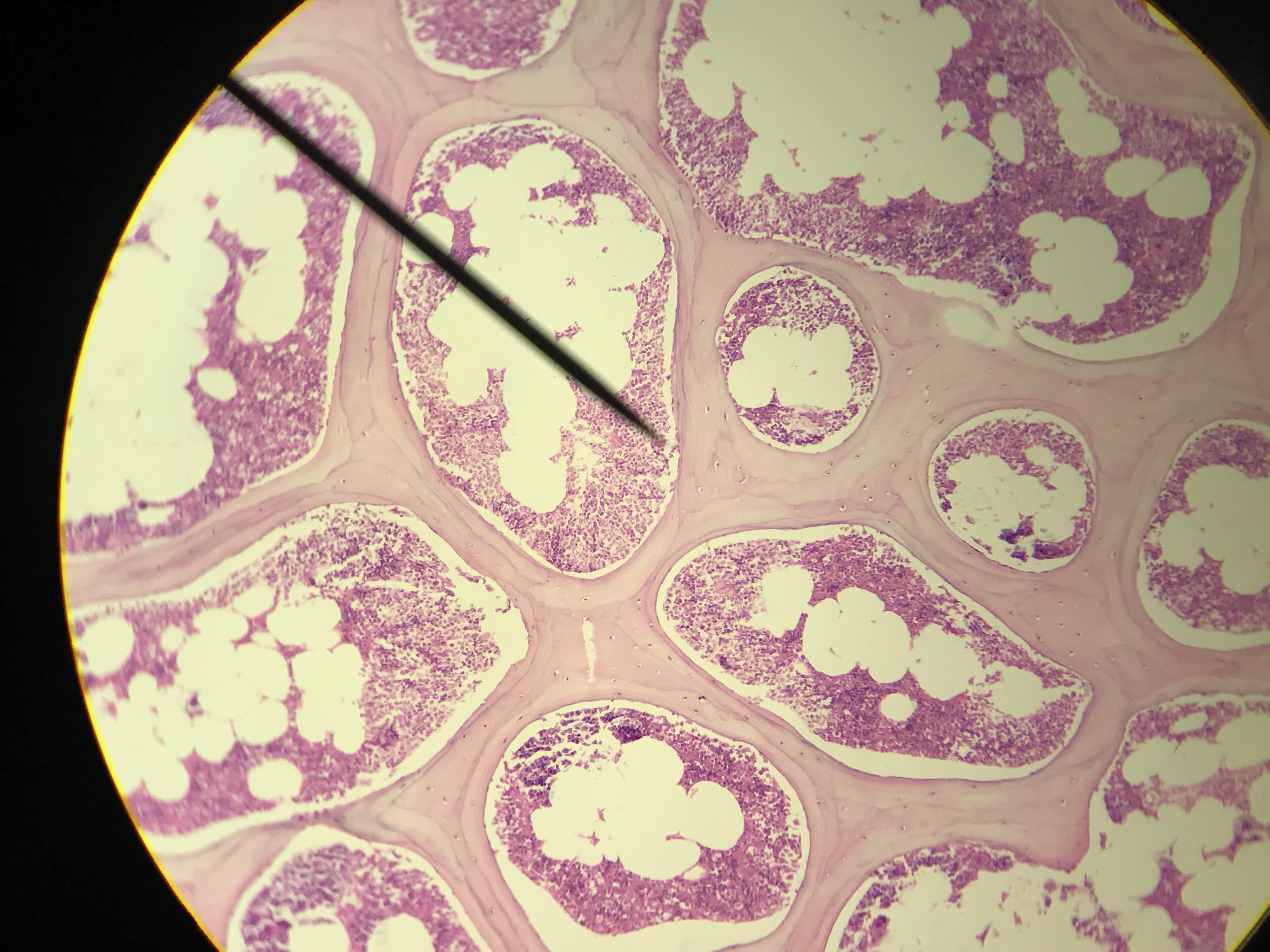
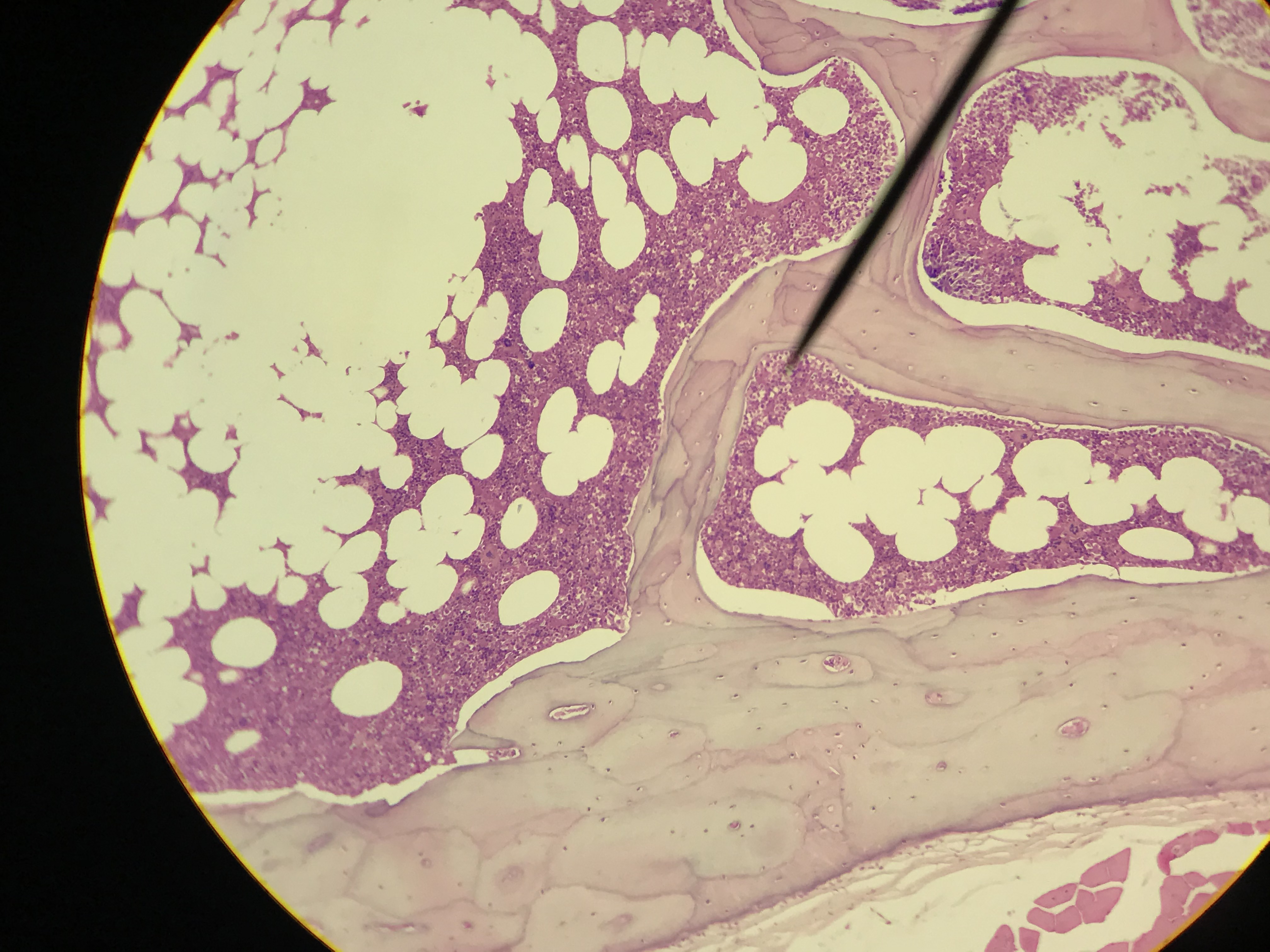
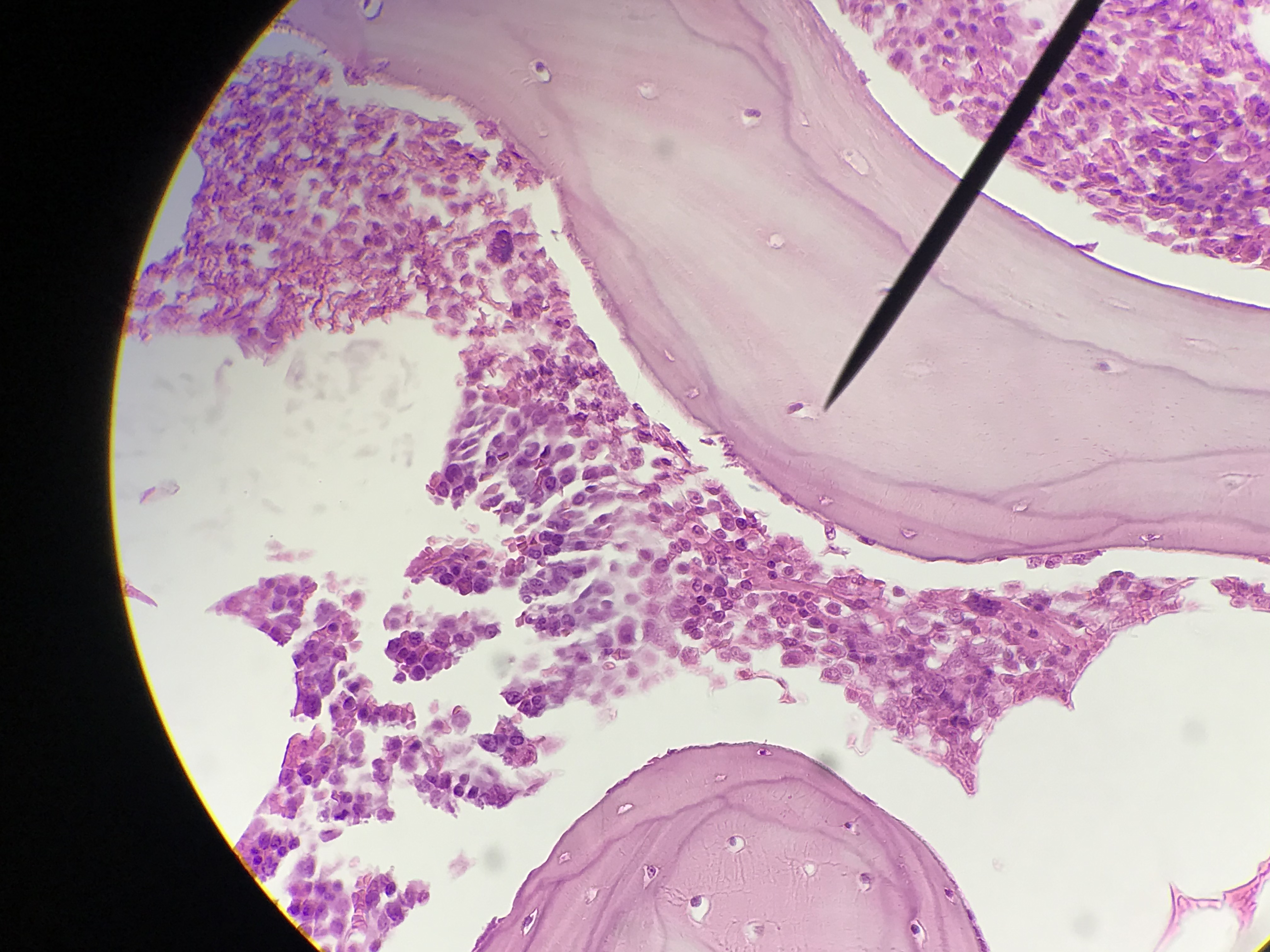
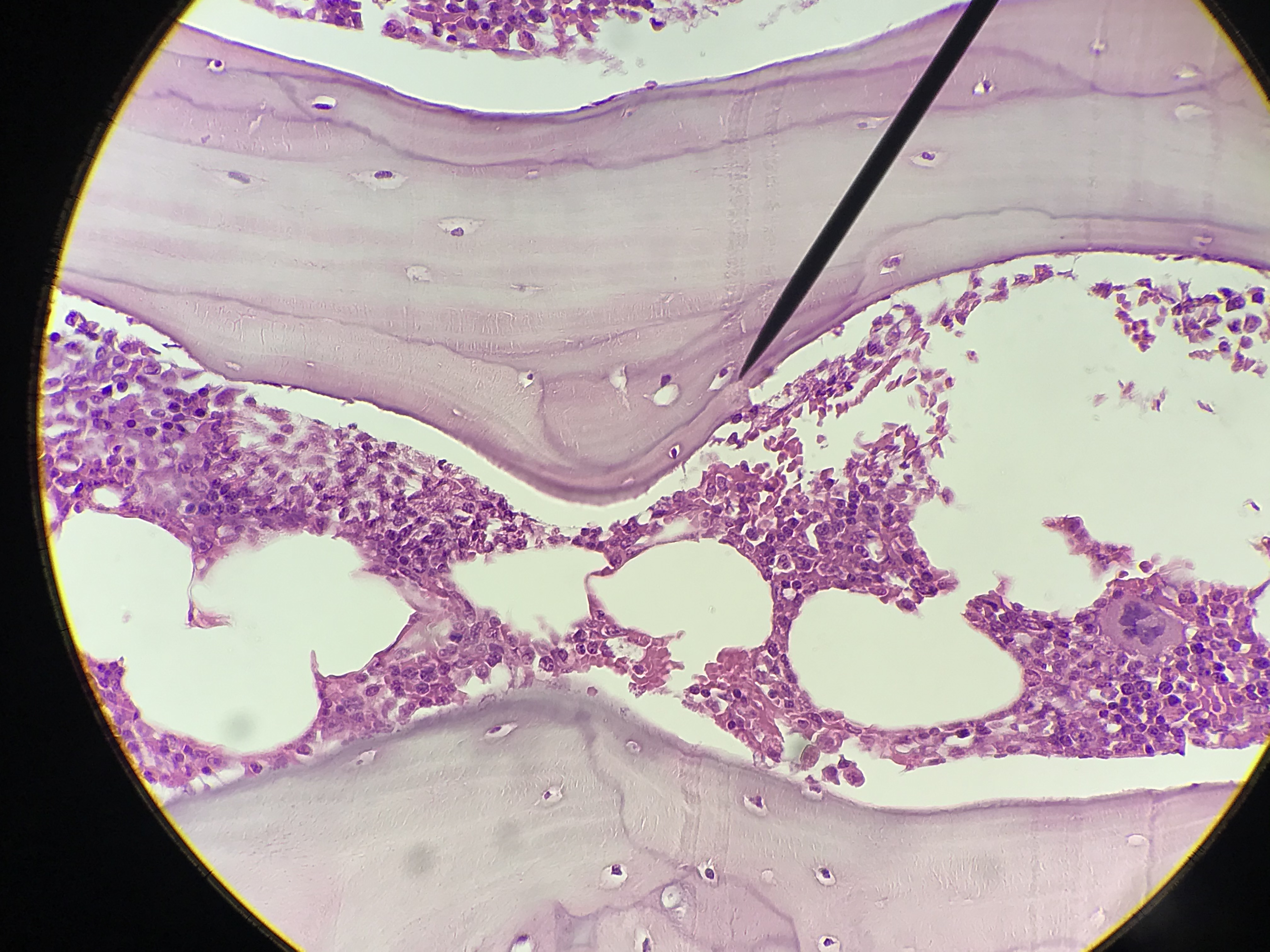
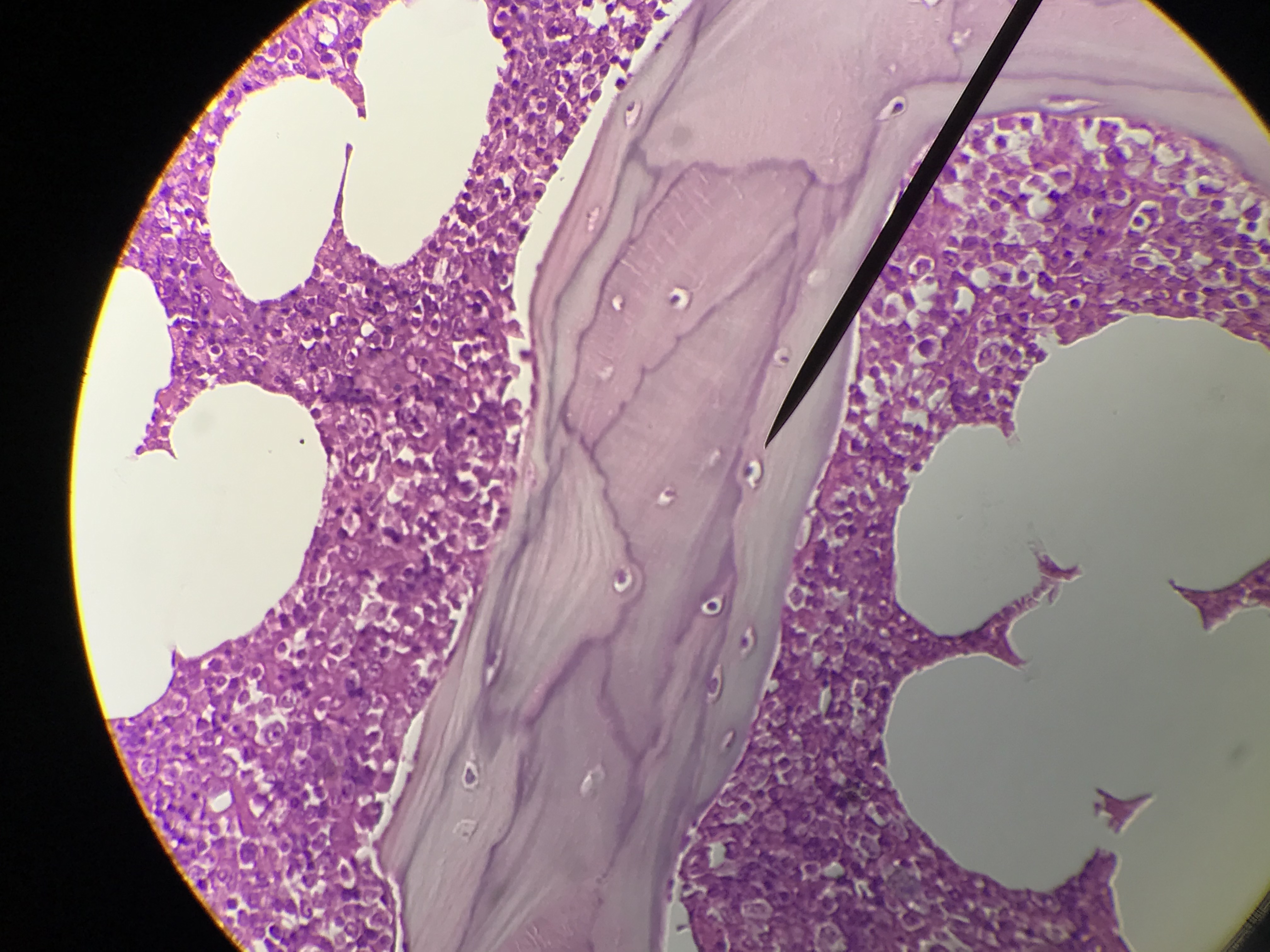
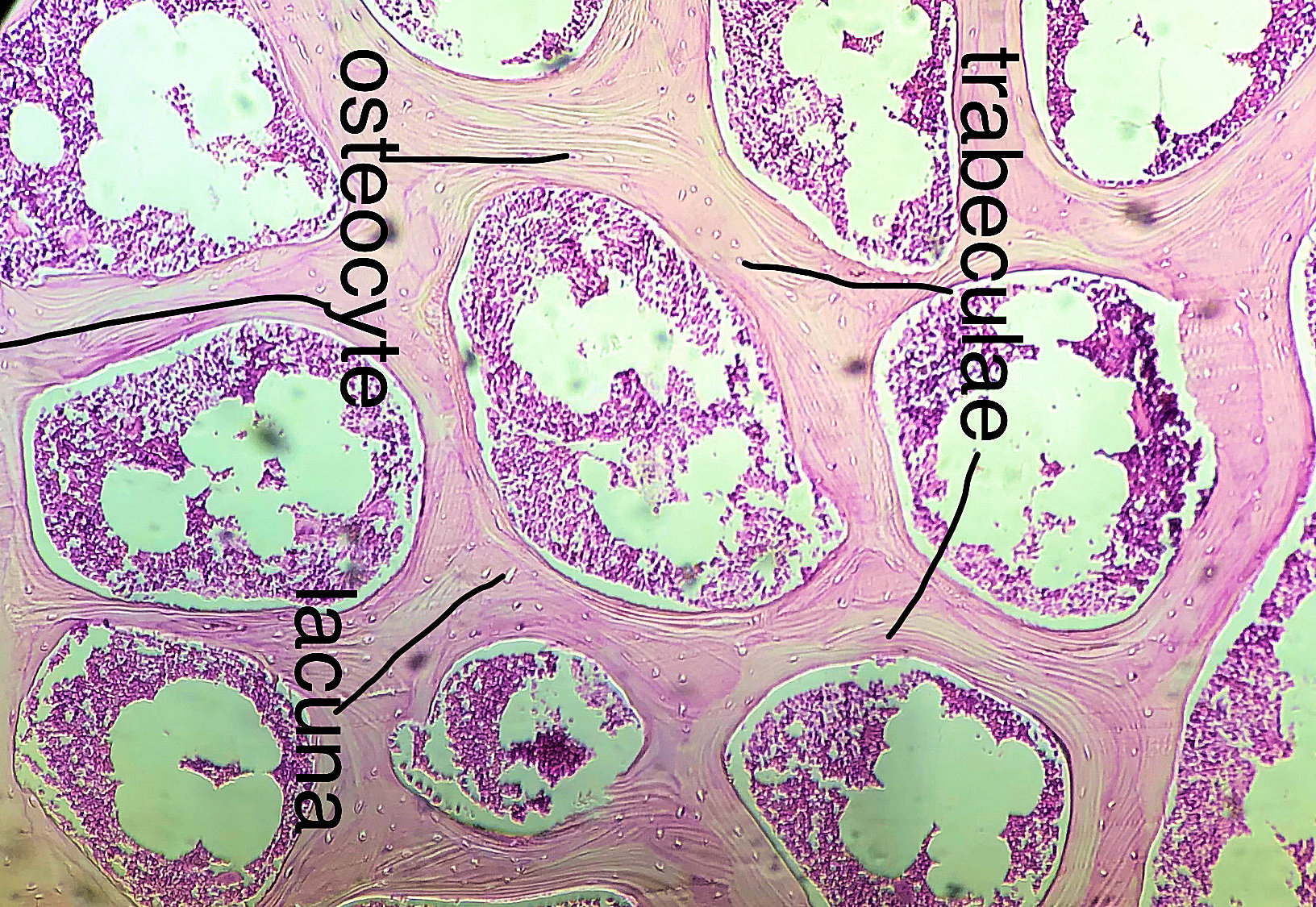
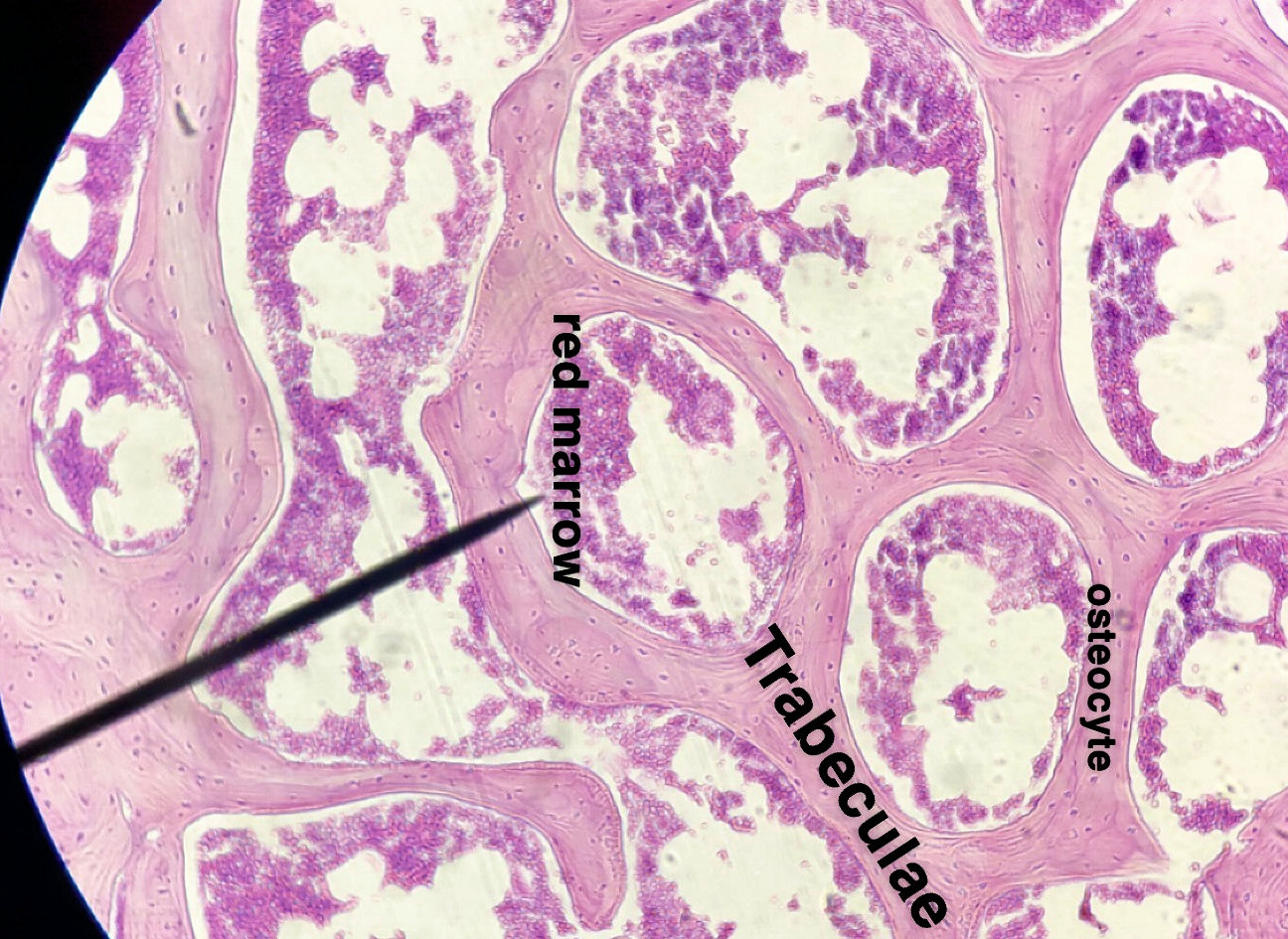
Spongy bone (AKA trabecular or cancellous bone) gets its name due to its porous (sponge like) nature. Instead of repeated units of osteons, Spongy bone is arranged in lattice like trabecula that have osteocytes randomly found in lacuna. You will not see any canals since the cells are typically only 2 or 3 layers deep and spongy bone is highly vascular. Spongy bone is found deep to compact bone. Due to space between trabecula Spongy bone is lighter in weight than compact bone. The trabecula offer support and transfer the load to the exterior (superficial) compact bone. Red bone marrow is found between the trabecula of some flat and long bones.
Slides on this page were made by students between the spring of 2018 and the spring of 2020. Go through
the diffrent student pictures and compare them to your lab book picture. Then slect one to draw on paper. Be sure
to label the cells, lacuna, fibers and other structures.
| Lab Book Image |
Student Images |
|
1 / 8
2 / 8
3/ 8
4 / 8
5 / 8
6 / 8
7 / 8
8 / 8
❮
❯
|

