Urinary Histology | Site Home Page
Renal Cortex
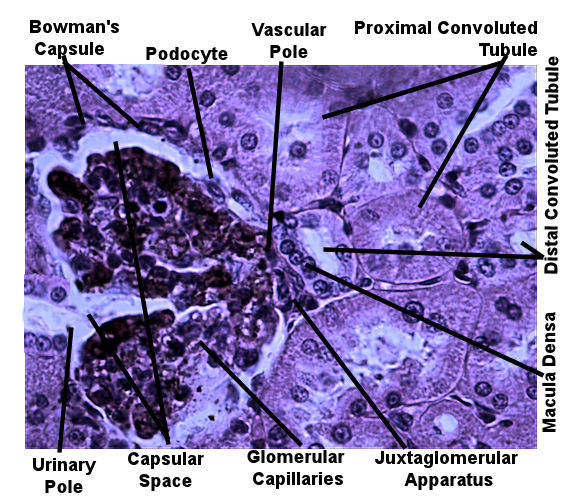
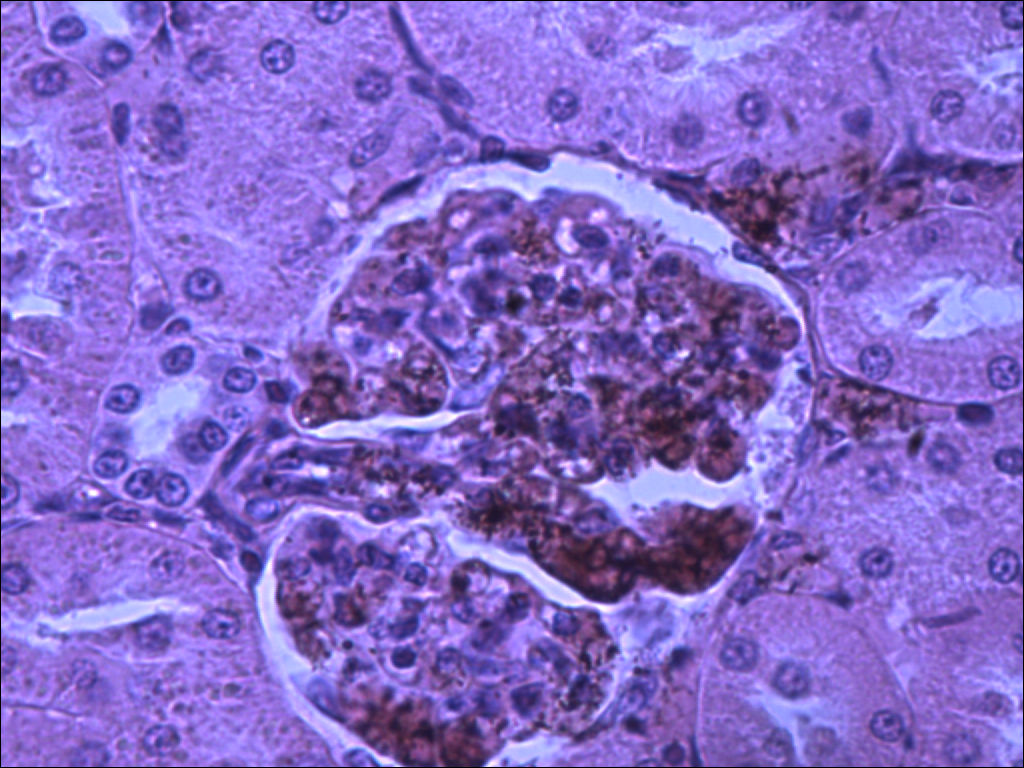
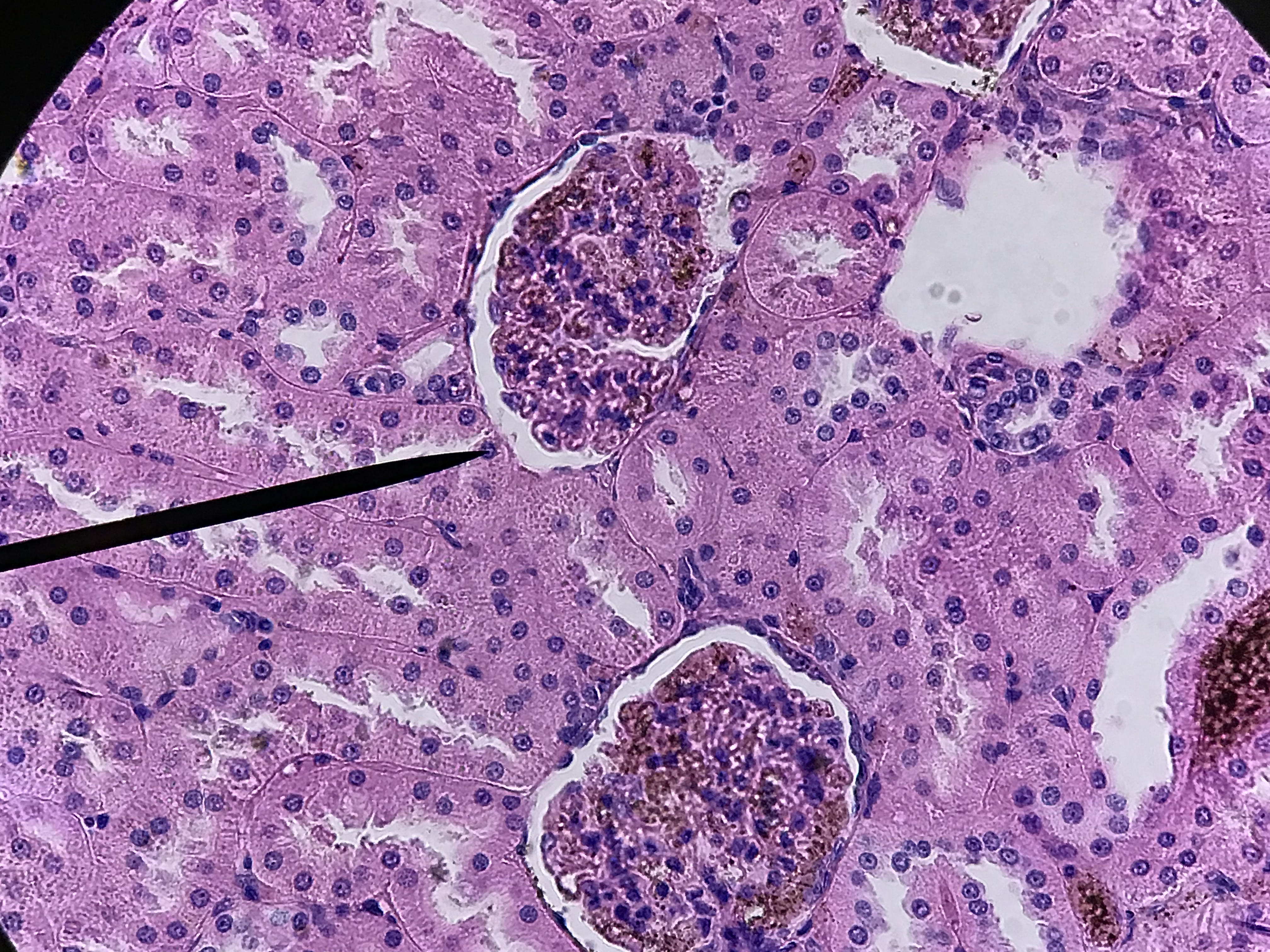
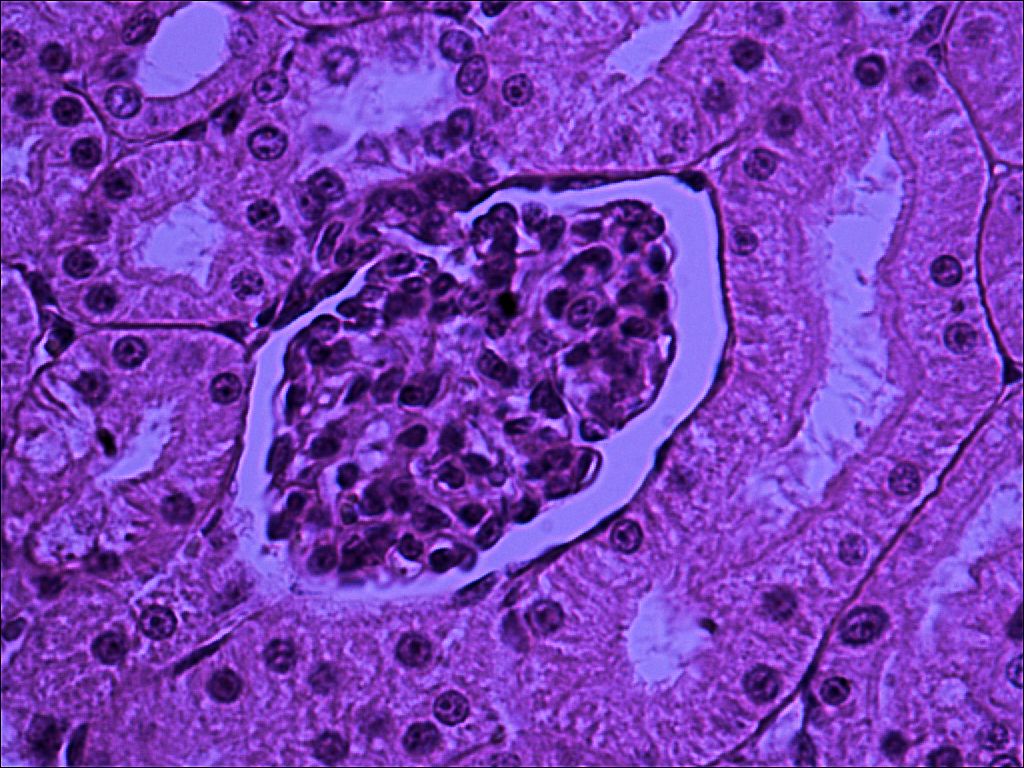
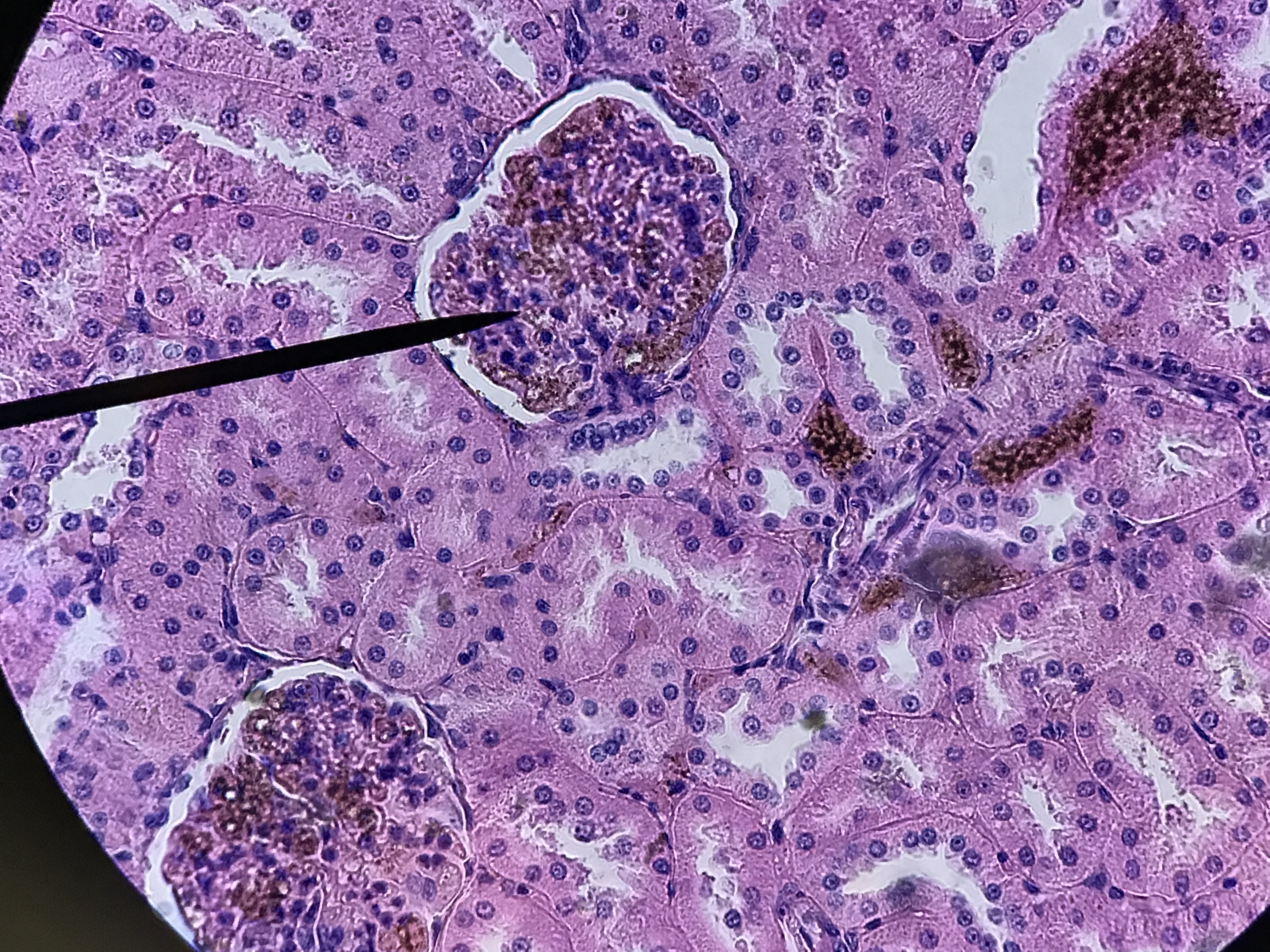
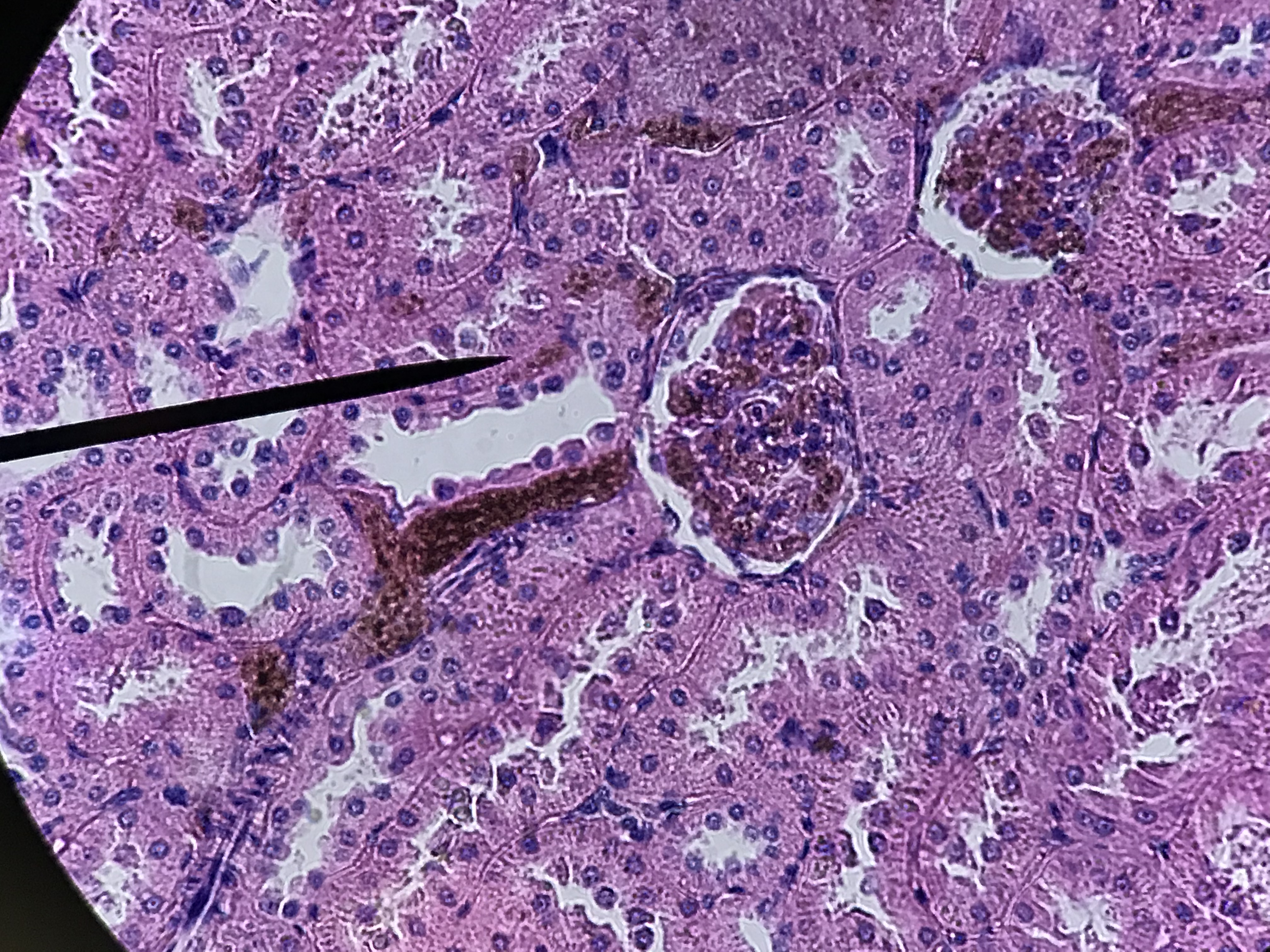
The arrangement of the tubules in the cortex will appear to be more random. That is because the convoluted tubules twist, turn, and wrap around the glomerulus which is a series of capillaries surrounded by the Bowman's capsule. Filtrate leaves the glomerular capillaries and enter the capsular space before it enters the proximal convoluted tubule. Proximal convoluted tubules are the larger tubule composed of simple cuboidal cells with microvilli and are therefore identifiable by being having large lumen with microvilli which causes the tubule to look blurry inside. The distal convoluted tubule tends to have a smaller diameter and lacks microvilli. There is always a distal convoluted tubule at the vascular pole of the glomerulus, which is the end in which the blood vessels enter. This distal convoluted tubule has columnar cells which make up the macula densa. These cells are typically close to the afferent arteriole and border on the juxtaglomerular apparatus which measures blood pressure. Opposite from the vascular pole is the urinary pole. Filtrate leaves the urinary pole from the capsular space and enters the proximal convoluted tubule. If observed under high enough magnification, you can observe podocytes surrounding the glomerular capillaries.
All pictures were taken by me under high power. This is a model
of what the cortex histology should look like. It may help you with structures. Look at the unlabeled pictures and try to find the structures
on the labeled picture. Then draw a picture and label it.
| Lab Book Image |
Unlabeled Images |
|
1 / 8
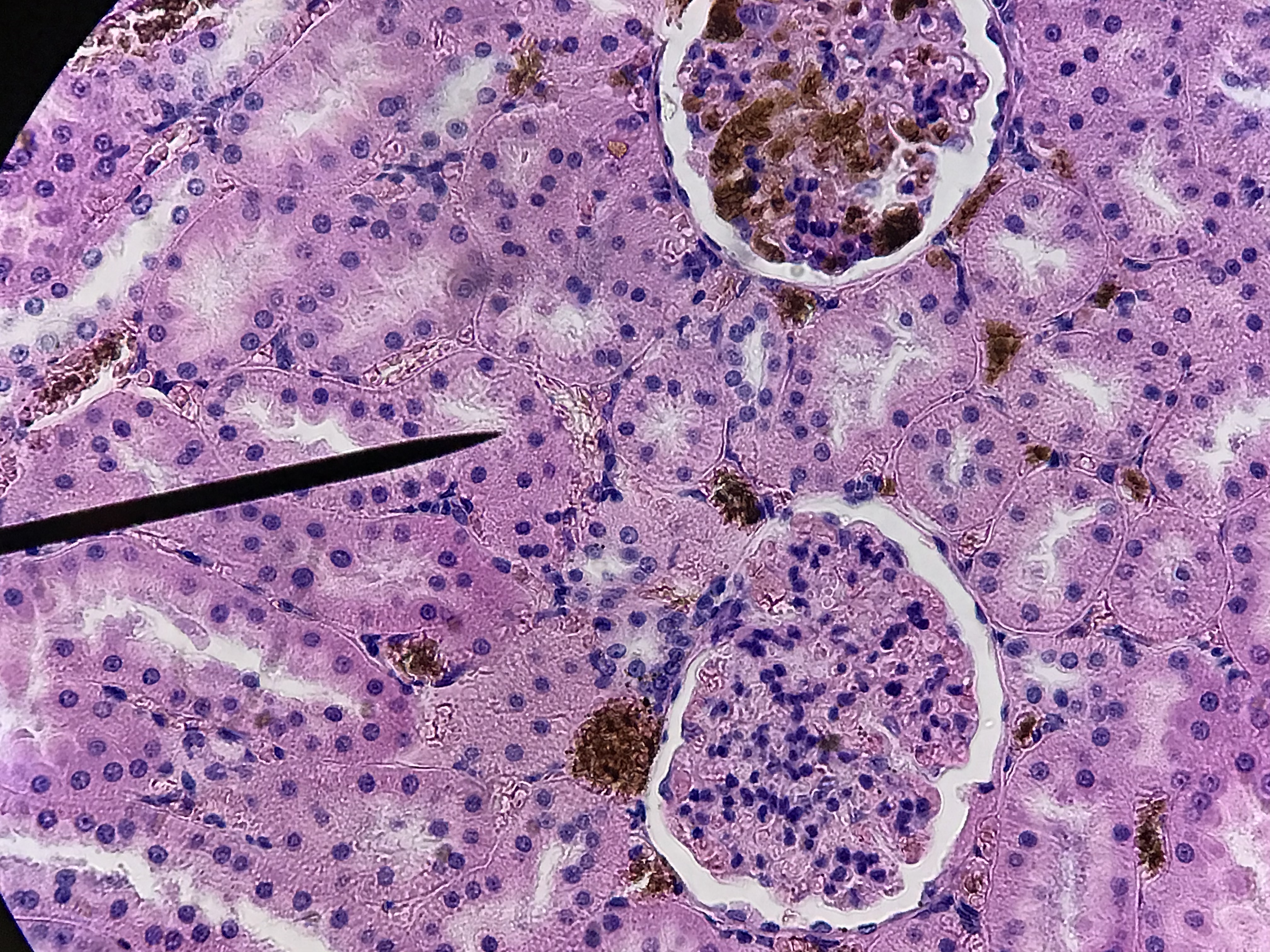
2 / 8
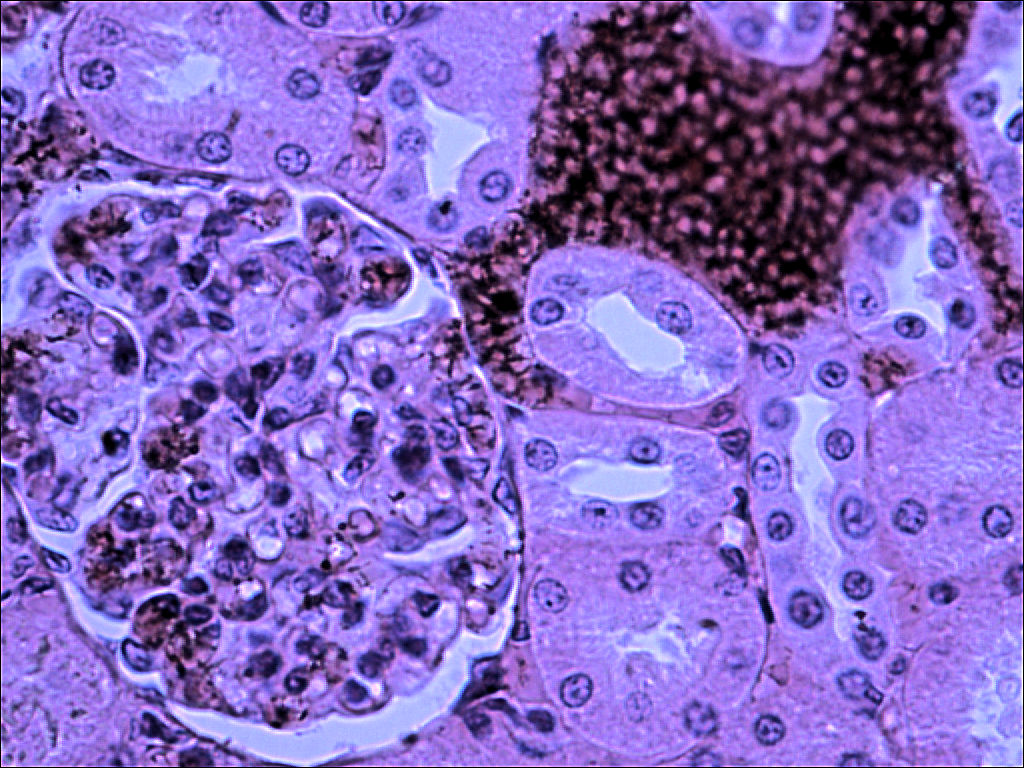
3/ 8
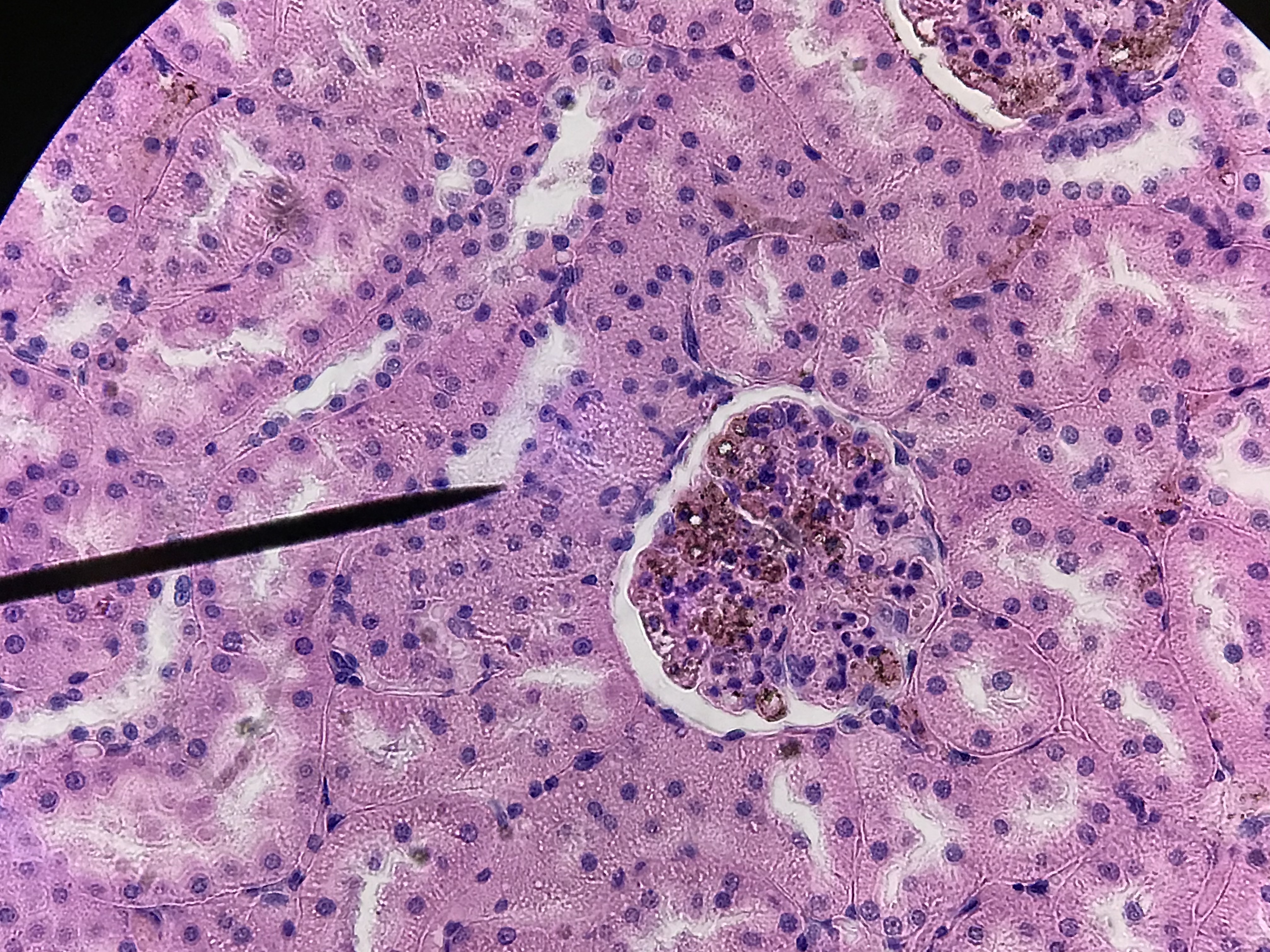
4 / 8
5 / 8
6 / 8
7 / 8
8 / 8
❮
❯
|

